From probiotics to fermentation: A review of microbes in food and supplements
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71320/bcs.0010Keywords:
Prebiotics, Postbiotics, Synbiotics, technological hurdles, global regulationsAbstract
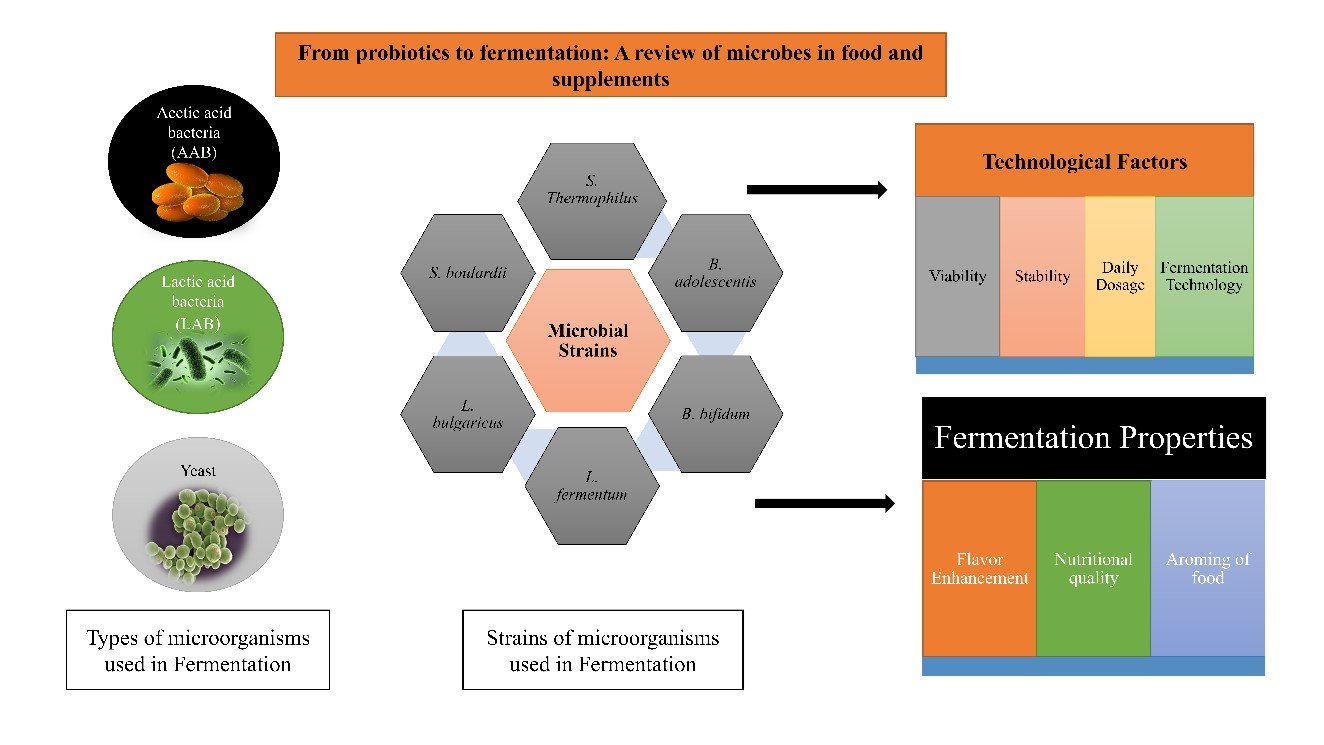
Microorganisms have a crucial role in processing food and preservation, as well as enhancing the nutritional and sensory qualities of food products. Microorganisms are utilized as additives for altering the nature of a substance and have a significant role in fermentation. Molds (e.g., Penicillium roqueforti and Geotrichum candidum), yeasts (e.g., Saccharomyces cerevisiae), and lactic acid bacteria are used to increase the shelf life of foodstuffs and the nutritional quality of processed foods in the fermentation process. Acetic acid bacteria and lactic acid bacteria are used in applied microbiology to increase the flavor of different manufactured foods. Further, bacteria, in the form of probiotics, are involved in the processing of food. Various strains of different bacteria are used as probiotics to increase the quality and preservation of foodstuffs. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are used to produce prebiotics and postbiotics as well. This article discusses the many ways that microorganisms may be added to food and supplements such as probiotics, prebiotics, postbiotics, and symbiotics in order to fulfill the world's food demand and make up for the scarcity of arable land. It also discusses the future prospects and challenges of this field.
References
Adedayo, M., Ajiboye, E., Akintunde, J., & Odaibo, A. (2011). Single cell proteins: as nutritional enhancer. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res, 2(5), 396-409.
Aderiye, B. I., & Laleye, S. A. (2003). Relevance of fermented food products in southwest Nigeria. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 58(3), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:QUAL.0000040315.02916.a3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:QUAL.0000040315.02916.a3
Ageitos, J. M., Vallejo, J. A., Veiga-Crespo, P., & Villa, T. G. (2011). Oily yeasts as oleaginous cell factories. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 90(4), 1219-1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3200-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3200-z
Agrawal, R. (2024). Production of Microbial Enzymes. In Textbook of Industrial Microbiology (pp. 233-277). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-9582-6_11 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-9582-6_11
Aguilar-Toalá, J. E., Garcia-Varela, R., Garcia, H. S., Mata-Haro, V., González-Córdova, A. F., Vallejo-Cordoba, B., & Hernández-Mendoza, A. (2018). Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 75, 105-114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.009
Aguirre-Garcia, Y. L., Nery-Flores, S. D., Campos-Muzquiz, L. G., Flores-Gallegos, A. C., Palomo-Ligas, L., Ascacio-Valdés, J. A., Sepúlveda-Torres, L., & Rodríguez-Herrera, R. (2024). Lactic Acid Fermentation in the Food Industry and Bio-Preservation of Food. Fermentation, 10(3), 168. https://www.mdpi.com/2311-5637/10/3/168 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030168
Ahire, J. J., Jakkamsetty, C., Kashikar, M. S., Lakshmi, S. G., & Madempudi, R. S. (2021). In Vitro Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus plantarum UBLP40 Isolated from Traditional Indigenous Fermented Food. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 13(5), 1413-1424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09775-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09775-7
Ahmed, H., Quentin, L., Ville, K., Olli, K., Sophie, L., Nathalie, D., & and Hanhineva, K. (2022). Microbiota-derived metabolites as drivers of gut–brain communication. Gut Microbes, 14(1), 2102878. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2022.2102878 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2022.2102878
Alvarez-Olmos, M. I., & Oberhelman, R. A. (2001). Probiotic agents and infectious diseases: a modern perspective on a traditional therapy. Clin Infect Dis, 32(11), 1567-1576. https://doi.org/10.1086/320518 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/320518
Ananou, S., Maqueda, M., Martínez-Bueno, M., & Valdivia, E. (2007). Biopreservation, an ecological approach to improve the safety and shelf-life of foods. Communicating current research and educational topics and trends in applied microbiology, 1(2), 475-487.
Anukam, K. C., & Reid, G. (2009). African traditional fermented foods and probiotics. J Med Food, 12(6), 1177-1184. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2008.0163 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2008.0163
Aravindan, R., Anbumathi, P., & Viruthagiri, T. (2007). Lipase applications in food industry. Indian Journal of Biotechnology, 6, 141-158.
Arora, S., Jood, S., & Khetarpaul, N. (2011). Effect of germination and probiotic fermentation on nutrient profile of pearl millet based food blends. British Food Journal, 113(4), 470-481. https://doi.org/10.1108/00070701111123952 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/00070701111123952
Ayseli, M. T., & İpek Ayseli, Y. (2016). Flavors of the future: Health benefits of flavor precursors and volatile compounds in plant foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 48, 69-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.11.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.11.005
Azais-Braesco, V., Bresson, J. L., Guarner, F., & Corthier, G. (2010). Not all lactic acid bacteria are probiotics, ...but some are. Br J Nutr, 103(7), 1079-1081. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510000723 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510000723
Baker, L. R., White, P. M., & Pierzynski, G. M. (2011). Changes in microbial properties after manure, lime, and bentonite application to a heavy metal-contaminated mine waste. Applied Soil Ecology, 48(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.02.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.02.007
Bartkiene, E., Ozogul, F., & Rocha, J. M. (2022). Bread Sourdough Lactic Acid Bacteria-Technological, Antimicrobial, Toxin-Degrading, Immune System-, and Faecal Microbiota-Modelling Biological Agents for the Preparation of Food, Nutraceuticals and Feed. Foods, 11(3), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030452 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030452
Bartowsky, E. J., & Henschke, P. A. (2008). Acetic acid bacteria spoilage of bottled red wine -- a review. Int J Food Microbiol, 125(1), 60-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.10.016 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.10.016
Bintsis, T. (2018). Lactic acid bacteria as starter cultures: An update in their metabolism and genetics. AIMS microbiology, 4(4), 665–684. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2018.4.665 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2018.4.665
Blanco, C. A., Caballero, I., Barrios, R., & Rojas, A. (2014). Innovations in the brewing industry: light beer. Int J Food Sci Nutr, 65(6), 655-660. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2014.893285 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2014.893285
Blandino, A., Al-Aseeri, M., Pandiella, S., Cantero, D., & Webb, C. (2003). Cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Food research international, 36(6), 527-543. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-9969(03)00009-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-9969(03)00009-7
Bondia-Pons, I., Nordlund, E., Mattila, I., Katina, K., Aura, A. M., Kolehmainen, M., Oresic, M., Mykkanen, H., & Poutanen, K. (2011). Postprandial differences in the plasma metabolome of healthy Finnish subjects after intake of a sourdough fermented endosperm rye bread versus white wheat bread. Nutr J, 10, 116. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-10-116 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-10-116
Braga, A., & Belo, I. (2022). Microbial Production of Flavors and Fragrances by Yarrowia lipolytica. In S. M. Jafari & F. D. Harzevili (Eds.), Microbial Production of Food Bioactive Compounds (pp. 1-28). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81403-8_7-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81403-8_7-1
Capozzi, V., Russo, P., Duenas, M. T., Lopez, P., & Spano, G. (2012). Lactic acid bacteria producing B-group vitamins: a great potential for functional cereals products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 96(6), 1383-1394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4440-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4440-2
Chang, Y., Jeong, C., Cheng, W., Choi, Y., Shin, D., Lee, S., & Han, S. (2021). Quality characteristics of yogurts fermented with short-chain fatty acid-producing probiotics and their effects on mucin production and probiotic adhesion onto human colon epithelial cells. Journal of Dairy Science, 104(7), 7415-7425. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-19820 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-19820
Chen, W., Lv, X., Tran, V.-T., Maruyama, J.-i., Han, K.-H., & Yu, J.-H. (2022). Editorial: From Traditional to Modern: Progress of Molds and Yeasts in Fermented-Food Production [Editorial]. Frontiers in Microbiology, Volume 13 - 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.876872 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.876872
Chu, Y., Li, M., Jin, J., Dong, X., Xu, K., Jin, L., Qiao, Y., & Ji, H. (2023). Advances in the Application of the Non-Conventional Yeast Pichia kudriavzevii in Food and Biotechnology Industries. J Fungi (Basel), 9(2), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020170 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020170
Dan, T., Ren, W., Liu, Y., Tian, J., Chen, H., Li, T., & Liu, W. (2019). Volatile Flavor Compounds Profile and Fermentation Characteristics of Milk Fermented by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Front Microbiol, 10, 2183. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02183 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02183
Das, A., Raychaudhuri, U., & Chakraborty, R. (2012). Cereal based functional food of Indian subcontinent: a review. J Food Sci Technol, 49(6), 665-672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0474-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0474-1
de Las Rivas, B., Rodriguez, H., Anguita, J., & Munoz, R. (2019). Bacterial tannases: classification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 103(2), 603-623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9519-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9519-y
Doron, S., & Gorbach, S. L. (2006). Probiotics: their role in the treatment and prevention of disease. Expert review of anti-infective therapy, 4(2), 261-275. https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.4.2.261 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.4.2.261
El-Shall, H. S., Shoukry, A. A., Abd El-Aleim, M. H., & Elsebaay, H. H. (2022). Extracellular lipase production by local isolate of Penicillium citrinum. Al-Azhar Journal of Agricultural Research, 47(1), 68-78. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajar.2022.266485 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21608/ajar.2022.266485
Ezendam, J., & van Loveren, H. (2006). Probiotics: immunomodulation and evaluation of safety and efficacy. Nutr Rev, 64(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00168.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00168.x
Ferrocino, I., Rantsiou, K., McClure, R., Kostic, T., de Souza, R. S. C., Lange, L., FitzGerald, J., Kriaa, A., Cotter, P., Maguin, E., Schelkle, B., Schloter, M., Berg, G., Sessitsch, A., Cocolin, L., & Consortium, T. M. (2023). The need for an integrated multi-OMICs approach in microbiome science in the food system. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 22(2), 1082-1103. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.13103 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.13103
FMI. (2025). Global Beverage Flavoring Market to Reach USD 9.1 Billion by 2035 Amid Rising Demand for Innovative and Natural Flavors. Future Market Insights, Inc. Retrieved April 30 from https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/03/21/3046972/0/en/Global-Beverage-Flavoring-Market-to-Reach-USD-9-1-Billion-by-2035-Amid-Rising-Demand-for-Innovative-and-Natural-Flavors-Future-Market-Insights-Inc.html
Galli, S. J., Metz, M., Starkl, P., Marichal, T., & Tsai, M. (2020). Mast cells and IgE in defense against lethality of venoms: Possible "benefit" of allergy[]. Allergo J Int, 29(2), 46-62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-020-00118-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40629-020-00118-6
Gangaraju, D., Raghu, A. V., & Siddalingaiya Gurudutt, P. (2022). Green synthesis of γ‐aminobutyric acid using permeabilized probiotic Enterococcus faecium for biocatalytic application. Nano Select, 3(10), 1436-1447. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202200059
Gibson, G. R., & Roberfroid, M. B. (1995). Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr, 125(6), 1401-1412. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/125.6.1401 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/125.6.1401
Gonzalez, A., Guillamon, J. M., Mas, A., & Poblet, M. (2006). Application of molecular methods for routine identification of acetic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol, 108(1), 141-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.10.025 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.10.025
Gorbach, S. L. (2000). Probiotics and gastrointestinal health. Am J Gastroenterol, 95(1 Suppl), S2-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9270(99)00806-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9270(99)00806-0
Graham, A. E., & Ledesma-Amaro, R. (2023). The microbial food revolution. Nature Communications, 14(1), 2231. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37891-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37891-1
Guerra, A. F., Lemos Junior, W. J. F., Santos, G. O. d., Andrighetto, C., Gianomini, A., Corich, V., & Luchese, R. H. (2018). Lactobacillus paracasei probiotic properties and survivability under stress-induced by processing and storage of ice cream bar or ice-lolly. Ciência Rural, 48. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20170601 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20170601
Gullo, M., Caggia, C., De Vero, L., & Giudici, P. (2006). Characterization of acetic acid bacteria in “traditional balsamic vinegar”. International journal of food microbiology, 106(2), 209-212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.06.024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.06.024
Gupta, C., Prakash, D., & Gupta, S. (2015). A biotechnological approach to microbial based perfumes and flavours. J. Microbiol. Exp, 2(10.15406). DOI: https://doi.org/10.15406/jmen.2015.02.00034
Gupta, V., & Garg, R. (2009). Probiotics. Indian J Med Microbiol, 27(3), 202-209. https://doi.org/10.4103/0255-0857.53201 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0255-0857.53201
Gurung, N., Ray, S., Bose, S., & Rai, V. (2013). A broader view: microbial enzymes and their relevance in industries, medicine, and beyond. BioMed research international, 2013(2013), 329121. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/329121 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/329121
Han, S., Zhang, J., & Jing, Y. (2020). Progress in Research about the Protease Extracted from Microorganisms. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 41(13), 321-327. https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.13.051
Hanft, F., & Koehler, P. (2006). Studies on the effect of glucose oxidase in bread making. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 86(11), 1699-1704. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2455 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2455
Hayek, S. A., Gyawali, R., Aljaloud, S. O., Krastanov, A., & Ibrahim, S. A. (2019). Cultivation media for lactic acid bacteria used in dairy products. J Dairy Res, 86(4), 490-502. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002202991900075X DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S002202991900075X
Hayek, S. A., & Ibrahim, S. A. (2013). Current Limitations and Challenges with Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Review. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 04(11), 73-87. https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2013.411A010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2013.411A010
Hosseini, S. F., Ansari, B., & Gharsallaoui, A. (2022). Polyelectrolytes-stabilized liposomes for efficient encapsulation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and improvement of its survivability under adverse conditions. Food Chem, 372, 131358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131358 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131358
Hu, Y., Zhang, L., Wen, R., Chen, Q., & Kong, B. (2022). Role of lactic acid bacteria in flavor development in traditional Chinese fermented foods: A review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 62(10), 2741-2755. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1858269 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1858269
Hua, S., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Zhou, Q., Li, Z., Liu, P., Wang, K., Zhu, Y., Han, D., & Yu, Y. (2024). Regulatory mechanisms of acetic acid, ethanol and high temperature tolerances of acetic acid bacteria during vinegar production. Microbial Cell Factories, 23(1), 324. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-024-02602-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-024-02602-y
Hutkins, R. W. (2006). Microbiology and Technology of Fermented Foods. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470277515 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470277515
Huwig, A., Freimund, S., Kappeli, O., & Dutler, H. (2001). Mycotoxin detoxication of animal feed by different adsorbents. Toxicol Lett, 122(2), 179-188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(01)00360-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(01)00360-5
Huynh, T. G., Shiu, Y. L., Nguyen, T. P., Truong, Q. P., Chen, J. C., & Liu, C. H. (2017). Current applications, selection, and possible mechanisms of actions of synbiotics in improving the growth and health status in aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 64, 367-382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.03.035 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.03.035
James, J., & Simpson, B. K. (1996). Application of enzymes in food processing. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 36(5), 437-463. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408399609527735 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408399609527735
Jiménez, N., Esteban-Torres, M., Mancheño, J. M., de Las Rivas, B., & Muñoz, R. (2014). Tannin degradation by a novel tannase enzyme present in some Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(10), 2991-2997. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00324-14 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00324-14
Jin, L. Z., Marquardt, R. R., & Zhao, X. (2000). A strain of Enterococcus faecium (18C23) inhibits adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 to porcine small intestine mucus. Appl Environ Microbiol, 66(10), 4200-4204. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.10.4200-4204.2000 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.10.4200-4204.2000
Jooyandeh, H., Amarjeet, K., & Minhas, K. (2009). Lipases in dairy industry: a review. Journal of Food Science and Technology (Mysore), 46(3), 181-189.
Kalsoom, M., Ur Rehman, F., Shafique, T., Junaid, S., Khalid, N., Adnan, M., Zafar, I., Abdullah Tariq, M., Raza, M. A., Zahra, A., & Ali, H. (2020). Biological Importance of Microbes in Agriculture, Food and Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review. Innovare Journal of Life Sciences, 8(6), 1-4. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijls.2020.v8i6.39845 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22159/ijls.2020.v8i6.39845
Kalui, C. M., Mathara, J. M., & Kutima, P. M. (2010). Probiotic potential of spontaneously fermented cereal based foods–A review. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9(17), 2490-2498.
Kårlund, A., Gómez-Gallego, C., Korhonen, J., Palo-Oja, O.-M., El-Nezami, H., & Kolehmainen, M. (2020). Harnessing microbes for sustainable development: Food fermentation as a tool for improving the nutritional quality of alternative protein sources. Nutrients, 12(4), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041020
Kim, Y. S., Kim, M. C., Kwon, S. W., Kim, S. J., Park, I. C., Ka, J. O., & Weon, H. Y. (2011). Analyses of bacterial communities in meju, a Korean traditional fermented soybean bricks, by cultivation-based and pyrosequencing methods. J Microbiol, 49(3), 340-348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-011-0302-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-011-0302-3
Latif, A., Shehzad, A., Niazi, S., Zahid, A., Ashraf, W., Iqbal, M. W., Rehman, A., Riaz, T., Aadil, R. M., & Khan, I. M. (2023). Probiotics: Mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Frontiers in microbiology, 14, 1216674. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1216674 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1216674
Leigh, S. J., Uhlig, F., Wilmes, L., Sanchez-Diaz, P., Gheorghe, C. E., Goodson, M. S., Kelley-Loughnane, N., Hyland, N. P., Cryan, J. F., & Clarke, G. (2023). The impact of acute and chronic stress on gastrointestinal physiology and function: a microbiota-gut-brain axis perspective. J Physiol, 601(20), 4491-4538. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP281951 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1113/JP281951
Lemos Junior, W. J. F., Fioravante Guerra, A., da Silva Duarte, V., Treu, L., Tarrah, A., Campanaro, S., Luchese, R. H., Giacomini, A., & Corich, V. (2019). Draft genome sequence data of Lactobacillus paracasei strain DTA83 isolated from infant stools. Data Brief, 22, 1064-1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.01.041 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.01.041
Leroy, F., & De Vuyst, L. (2004). Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 15(2), 67-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2003.09.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2003.09.004
Li, H.-Y., Zhou, D.-D., Gan, R.-Y., Huang, S.-Y., Zhao, C.-N., Shang, A., Xu, X.-Y., & Li, H.-B. (2021). Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 13(9), 3211. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/9/3211 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093211
Lilly, D. M., & Stillwell, R. H. (1965). Probiotics: Growth-Promoting Factors Produced by Microorganisms. Science, 147(3659), 747-748. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.147.3659.747 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.147.3659.747
Lind, H., Jonsson, H., & Schnurer, J. (2005). Antifungal effect of dairy propionibacteria--contribution of organic acids. Int J Food Microbiol, 98(2), 157-165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.05.020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.05.020
Luo, Y., De Souza, C., Ramachandran, M., Wang, S., Yi, H., Ma, Z., Zhang, L., & Lin, K. (2022). Precise oral delivery systems for probiotics: A review. J Control Release, 352, 371-384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.030
Macfarlane, G. T., & Macfarlane, S. (1997). Human colonic microbiota: ecology, physiology and metabolic potential of intestinal bacteria. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl, 222(sup222), 3-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365521.1997.11720708 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00365521.1997.11720708
Magnusson, J., Strom, K., Roos, S., Sjogren, J., & Schnurer, J. (2003). Broad and complex antifungal activity among environmental isolates of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 219(1), 129-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(02)01207-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(02)01207-7
Malimas, T., Yukphan, P., Takahashi, M., Muramatsu, Y., Kaneyasu, M., Potacharoen, W., Tanasupawat, S., Nakagawa, Y., Tanticharoen, M., & Yamada, Y. (2009). Gluconobacter japonicus sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium in the Alphaproteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 59(Pt 3), 466-471. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65740-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65740-0
Markowiak, P., & Śliżewska, K. (2017). Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients, 9(9), 1021. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/9/1021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9091021
Marsh, A. J., Hill, C., Ross, R. P., & Cotter, P. D. (2014). Fermented beverages with health-promoting potential: Past and future perspectives. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 38(2), 113-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.05.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.05.002
Mattila-Sandholm, T., Myllärinen, P., Crittenden, R., Mogensen, G., Fondén, R., & Saarela, M. (2002). Technological challenges for future probiotic foods. International Dairy Journal, 12(2-3), 173-182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00099-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00099-1
Maurya, R., Patel, H., Bhatt, D., Shakhreliya, S., Gohil, N., Bhattacharjee, G., Lam, N. L., Alzahrani, K. J., Gyanchander, E., & Singh, V. (2022). Microbial Production of Natural Flavors and Fragrances. In A. Kumar, K. Patruni, & V. Singh (Eds.), Recent Advances in Food Biotechnology (pp. 139-159). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8125-7_7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8125-7_7
McGhee, J. (1999). Mucosal immune responses. An overview. Mucosal immunology, 485-505.
McKevith, B. (2004). Nutritional aspects of cereals. Nutrition Bulletin, 29(2), 111-142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-3010.2004.00418.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-3010.2004.00418.x
Merenstein, D., Pot, B., Leyer, G., Ouwehand, A. C., Preidis, G. A., Elkins, C. A., Hill, C., Lewis, Z. T., Shane, A. L., Zmora, N., Petrova, M. I., Collado, M. C., Morelli, L., Montoya, G. A., Szajewska, H., Tancredi, D. J., & Sanders, M. E. (2023). Emerging issues in probiotic safety: 2023 perspectives. Gut microbes, 15(1), 2185034. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2023.2185034 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2023.2185034
Metchnikoff, E., & Chalmers-Mitchell, P. (1908). The Prolongation of Life. Optimistic studies. New York: GP Putnam's Sons. In: The Knickerbocker Press. Edited by P. Chalmers Mitchell.
Min, K. H., Yin, F. H., Amin, Z., Mansa, R. F., & Ling, C. (2022). An overview of the role of lactic acid bacteria in fermented foods and their potential probiotic properties. Borneo Int. J. Biotechnol, 2, 65-83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.51200/bijb.v2i.4186
Mishra, G., & Panda, B. K. (2022). Cereal Based Fermented Foods and Non-alcohol Beverages. In S. Punia Bangar & A. Kumar Siroha (Eds.), Functional Cereals and Cereal Foods: Properties, Functionality and Applications (pp. 189-213). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05611-6_8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05611-6_8
Mokoena, M. P., Chelule, P. K., & Gqaleni, N. (2005). Reduction of fumonisin B1 and zearalenone by lactic acid bacteria in fermented maize meal. J Food Prot, 68(10), 2095-2099. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x-68.10.2095 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-68.10.2095
Mosha, T. C., & Vicent, M. M. (2004). Nutritional value and acceptability of homemade maize/sorghum-based weaning mixtures supplemented with rojo bean flour, ground sardines and peanut paste. Int J Food Sci Nutr, 55(4), 301-315. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637480410001225184 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09637480410001225184
Mota de Carvalho, N., Costa, E. M., Silva, S., Pimentel, L., Fernandes, T. H., & Pintado, M. E. (2018). Fermented Foods and Beverages in Human Diet and Their Influence on Gut Microbiota and Health. Fermentation, 4(4), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4040090 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4040090
Mueed, A., Shibli, S., Korma, S. A., Madjirebaye, P., Esatbeyoglu, T., & Deng, Z. (2022). Flaxseed Bioactive Compounds: Chemical Composition, Functional Properties, Food Applications and Health Benefits-Related Gut Microbes. Foods, 11(20), 3307. https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/11/20/3307 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11203307
Mukherjee, A., Gomez-Sala, B., O'Connor, E. M., Kenny, J. G., & Cotter, P. D. (2022). Global Regulatory Frameworks for Fermented Foods: A Review. Front Nutr, 9, 902642. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.902642 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.902642
Muradova, M., Proskura, A., Canon, F., Aleksandrova, I., Schwartz, M., Heydel, J.-M., Baranenko, D., Nadtochii, L., & Neiers, F. (2023). Unlocking Flavor Potential Using Microbial β-Glucosidases in Food Processing. Foods, 12(24), 4484. https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/12/24/4484
Muradova, M., Proskura, A., Canon, F., Aleksandrova, I., Schwartz, M., Heydel, J. M., Baranenko, D., Nadtochii, L., & Neiers, F. (2023). Unlocking Flavor Potential Using Microbial beta-Glucosidases in Food Processing. Foods, 12(24), 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244484 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244484
Nout, M. J. (2009). Rich nutrition from the poorest - cereal fermentations in Africa and Asia. Food Microbiol, 26(7), 685-692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2009.07.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2009.07.002
Oyeleke, S. (2009). Microbial assessment of some commercially prepared yoghurt retailed in Minna, Niger State. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 3(5), 245-248.
Paulino, B. N., Sales, A., Felipe, L., Pastore, G. M., Molina, G., & Bicas, J. L. (2021). Recent advances in the microbial and enzymatic production of aroma compounds. Current Opinion in Food Science, 37, 98-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2020.09.010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2020.09.010
Petruzziello, C., Saviano, A., & Ojetti, V. (2023). Probiotics, the Immune Response and Acute Appendicitis: A Review. Vaccines (Basel), 11(7), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071170 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071170
Pikaar, I., Matassa, S., Bodirsky, B. L., Weindl, I., Humpenoder, F., Rabaey, K., Boon, N., Bruschi, M., Yuan, Z., van Zanten, H., Herrero, M., Verstraete, W., & Popp, A. (2018). Decoupling Livestock from Land Use through Industrial Feed Production Pathways. Environ Sci Technol, 52(13), 7351-7359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00216 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00216
Plaza-Diaz, J., Ruiz-Ojeda, F. J., Gil-Campos, M., & Gil, A. (2019). Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv Nutr, 10(suppl_1), S49-S66. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmy063 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmy063
Pswarayi, F., & Gänzle, M. (2022). African cereal fermentations: A review on fermentation processes and microbial composition of non-alcoholic fermented cereal foods and beverages. International journal of Food microbiology, 378, 109815. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109815
Quinto, E. J., Jiménez, P., Caro, I., Tejero, J., Mateo, J., & Girbés, T. (2014). Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Review. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 05(18), 1765-1775. https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2014.518190 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2014.518190
Rachwał, K., & Gustaw, K. (2024). Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sustainable Food Production. Sustainability, 16(8), 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083362 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083362
Raveendran, S., Parameswaran, B., Ummalyma, S. B., Abraham, A., Mathew, A. K., Madhavan, A., Rebello, S., & Pandey, A. (2018). Applications of Microbial Enzymes in Food Industry. Food Technol Biotechnol, 56(1), 16-30. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.56.01.18.5491 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.56.01.18.5491
Razavi, S., Janfaza, S., Tasnim, N., Gibson, D. L., & Hoorfar, M. (2021). Microencapsulating polymers for probiotics delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Food Hydrocolloids, 120, 106882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106882 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106882
Regalado, C., García-Almendárez, B. E., & Duarte-Vázquez, M. A. (2004). Biotechnological applications of peroxidases. Phytochemistry Reviews, 3(1-2), 243-256. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:Phyt.0000047797.81958.69 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHYT.0000047797.81958.69
Reid, G., Jass, J., Sebulsky, M. T., & McCormick, J. K. (2003). Potential uses of probiotics in clinical practice. Clin Microbiol Rev, 16(4), 658-672. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.16.4.658-672.2003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.16.4.658-672.2003
Reque, P. M., Pinilla, C. M. B., Gauterio, G. V., Kalil, S. J., & Brandelli, A. (2019). Xylooligosaccharides production from wheat middlings bioprocessed with Bacillus subtilis. Food Res Int, 126, 108673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108673 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108673
Román, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 67, 44-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.06.010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.06.010
Romano, P., Braschi, G., Siesto, G., Patrignani, F., & Lanciotti, R. (2022). Role of Yeasts on the Sensory Component of Wines. Foods, 11(13), 1921. https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/11/13/1921 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131921
Rosenstock, E., Ebert, J., & Scheibner, A. (2021). Cultured Milk: Fermented Dairy Foods along the Southwest Asian–European Neolithic Trajectory. Current Anthropology, 62(S24), S256-S275. https://doi.org/10.1086/714961 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/714961
Saber, A., Alipour, B., Faghfoori, Z., & Yari Khosroushahi, A. (2017). Cellular and molecular effects of yeast probiotics on cancer. Crit Rev Microbiol, 43(1), 96-115. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2016.1179622 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2016.1179622
Sadishkumar, V., & Jeevaratnam, K. (2016). In vitro probiotic evaluation of potential antioxidant lactic acid bacteria isolated from idli batter fermented with Piper betle leaves. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 52(2), 329-340. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13284 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13284
Saghir, S. A. M., & Suede, F. S. A. (2024). Synergistic Efficacy and Mechanism of Probiotics and Prebiotics in Enhancing Health Impact. Microbial Bioactives, 7(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.25163/microbbioacts.719300 DOI: https://doi.org/10.25163/microbbioacts.719300
Samanta, S. (2022). Potential Impacts of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Cancer Prevention. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 22(4), 605-628. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520621999201210220442 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520621999201210220442
Santos, F., Wegkamp, A., de Vos, W. M., Smid, E. J., & Hugenholtz, J. (2008). High-Level folate production in fermented foods by the B12 producer Lactobacillus reuteri JCM1112. Appl Environ Microbiol, 74(10), 3291-3294. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02719-07 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02719-07
Schnürer, J., & Magnusson, J. (2005). Antifungal lactic acid bacteria as biopreservatives. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 16(1-3), 70-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2004.02.014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2004.02.014
Sengun, I. Y., & Karabiyikli, S. (2011). Importance of acetic acid bacteria in food industry. Food control, 22(5), 647-656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.11.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.11.008
Senok, A. C., Ismaeel, A. Y., & Botta, G. A. (2005). Probiotics: facts and myths. Clin Microbiol Infect, 11(12), 958-966. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01228.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01228.x
Settanni, L., & Corsetti, A. (2008). Application of bacteriocins in vegetable food biopreservation. Int J Food Microbiol, 121(2), 123-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.09.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.09.001
Shamekhi, S., Abdolalizadeh, J., Ostadrahimi, A., Mohammadi, S. A., Barzegari, A., Lotfi, H., Bonabi, E., & Zarghami, N. (2020). Apoptotic Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on Human Colon Cancer SW480 Cells by Regulation of Akt/NF-kB Signaling Pathway. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 12(1), 311-319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09528-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09528-7
Shojaei Zinjanab, M., Golmakani, M. T., Eskandari, M. H., Toh, M., & Liu, S. Q. (2021). Natural flavor biosynthesis by lipase in fermented milk using in situ produced ethanol. J Food Sci Technol, 58(5), 1858-1868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04697-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04697-8
Siddiqui, S. A., Erol, Z., Rugji, J., Taşçı, F., Kahraman, H. A., Toppi, V., Musa, L., Di Giacinto, G., Bahmid, N. A., Mehdizadeh, M., & Castro-Muñoz, R. (2023). An overview of fermentation in the food industry - looking back from a new perspective. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 10(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-023-00702-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-023-00702-y
Singh, V., Singh, N., Verma, M., Praveena, S. M., Verma, M. K., Bilal, M., Singh, M. P., & Mishra, V. (2022). Nanotechnology in agriculture and bioencapsulation of probiotics/food additives. In Smart nanomaterials for bioencapsulation (pp. 213-223). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91229-7.00011-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91229-7.00011-8
Slingerland, M. A., Traore, K., Kayodé, A. P. P., & Mitchikpe, C. E. S. (2021). Fighting Fe deficiency malnutrition in West Africa: an interdisciplinary programme on a food chain approach. NJAS: Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences, 53(3-4), 253-279. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1573-5214(06)80009-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1573-5214(06)80009-6
So, S. S., Wan, M. L., & El-Nezami, H. (2017). Probiotics-mediated suppression of cancer. Curr Opin Oncol, 29(1), 62-72. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCO.0000000000000342 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/CCO.0000000000000342
Stanton, C., Gardiner, G., Meehan, H., Collins, K., Fitzgerald, G., Lynch, P. B., & Ross, R. P. (2001). Market potential for probiotics. Am J Clin Nutr, 73(2 Suppl), 476S-483S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/73.2.476s DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/73.2.476s
Strachel, R., Wyszkowska, J., & Bacmaga, M. (2017). The Role of Compost in Stabilizing the Microbiological and Biochemical Properties of Zinc-Stressed Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut, 228(9), 349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3539-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3539-6
Sukaew, T. (2024). The Current and Emerging Research Related Aroma and Flavor. In R. S. Samakradhamrongthai (Ed.), Aroma and Flavor in Product Development: Characterization, Perception, and Application (pp. 329-369). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62612-8_11 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62612-8_11
Sukumaran, R. K., Singhania, R. R., & Pandey, A. (2005). Microbial cellulases-production, applications and challenges. Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research, 64, 832-844.
Thakkar, P. N., Modi, H. A., & Prajapati, J. (2016). Therapeutic Impacts of Probiotics--as Magic Bullet. American Journal of Biomedical Sciences, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.5099/aj160200097 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5099/aj160200097
Tomasik, P., & Tomasik, P. (2020). Probiotics, Non-Dairy Prebiotics and Postbiotics in Nutrition. Applied Sciences, 10(4), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041470 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041470
Varga, J., Peteri, Z., Tabori, K., Teren, J., & Vagvolgyi, C. (2005). Degradation of ochratoxin A and other mycotoxins by Rhizopus isolates. Int J Food Microbiol, 99(3), 321-328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.10.034 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.10.034
Vassilev, N., Martos, E., Mendes, G., Martos, V., & Vassileva, M. (2013). Biochar of animal origin: a sustainable solution to the global problem of high-grade rock phosphate scarcity? J Sci Food Agric, 93(8), 1799-1804. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6130 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6130
Vera-Santander, V. E., Hernández-Figueroa, R. H., Jiménez-Munguía, M. T., Mani-López, E., & López-Malo, A. (2023). Health Benefits of Consuming Foods with Bacterial Probiotics, Postbiotics, and Their Metabolites: A Review. Molecules, 28(3), 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031230 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031230
Wang, Y., Trani, A., Knaapila, A., Hietala, S., Coda, R., Katina, K., & Maina, N. H. (2020). The effect of in situ produced dextran on flavour and texture perception of wholegrain sorghum bread. Food Hydrocolloids, 106, 105913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105913 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105913
Wouters, J. T. M., Ayad, E. H. E., Hugenholtz, J., & Smit, G. (2002). Microbes from raw milk for fermented dairy products. International Dairy Journal, 12(2-3), 91-109. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0958-6946(01)00151-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00151-0
Xu, C., Ban, Q., Wang, W., Hou, J., & Jiang, Z. (2022). Novel nano-encapsulated probiotic agents: Encapsulate materials, delivery, and encapsulation systems. J Control Release, 349, 184-205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.061 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.061
Yadav, H., Singh, S., & Sinha, R. (2024). Fermentation Technology for Microbial Products and Their Process Optimization. In P. Verma (Ed.), Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology: A New Horizon of the Microbial World (pp. 35-64). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-6270-5_2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-6270-5_2
Yamada, Y., & Yukphan, P. (2008). Genera and species in acetic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol, 125(1), 15-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.11.077 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.11.077
Yassunaka Hata, N. N., Surek, M., Sartori, D., Vassoler Serrato, R., & Aparecida Spinosa, W. (2023). Role of acetic acid bacteria in food and beverages. Food technology and biotechnology, 61(1), 85-103. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.61.01.23.7811
Zakaria, S. M., & Kamal, S. M. M. (2015). Subcritical Water Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Plants and Algae: Applications in Pharmaceutical and Food Ingredients. Food Engineering Reviews, 8(1), 23-34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-015-9119-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-015-9119-x
Zhu, Z., Momeu, C., Zakhartsev, M., & Schwaneberg, U. (2006). Making glucose oxidase fit for biofuel cell applications by directed protein evolution. Biosens Bioelectron, 21(11), 2046-2051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2005.11.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2005.11.018
Published
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bio Communications

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © Bio Communications. This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) license. Under this license, you are free to share (copy and redistribute) this material in any medium or format for non-commercial purposes, provided you give appropriate credit to the author(s) and the journal. No modifications or adaptations of the material are permitted. The copyright for this article remains with the journal Bio Communications.







 .
.